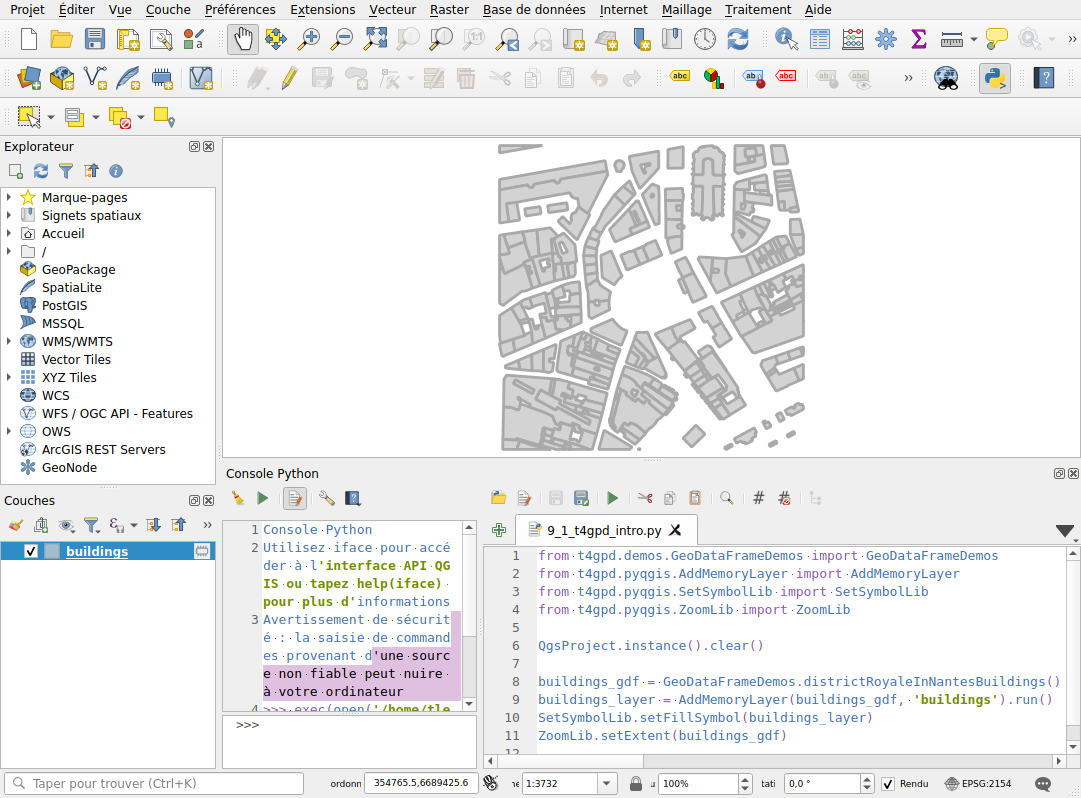
Interfacing with QGIS (version 0.3.0+)
Provided you have correctly configured your QGIS instance1, you can use the t4gpd plugin in the context of its Python console. Thus, the t4gpd.pyqgis.AddMemoryLayer class allows you to transform a GeoDataFrame into a qgis.core.QgsVectorLayer, and then add this new layer to the current qgis.core.QgsProject instance.
from t4gpd.demos.GeoDataFrameDemos import GeoDataFrameDemos
from t4gpd.pyqgis.AddMemoryLayer import AddMemoryLayer
from t4gpd.pyqgis.SetSymbolLib import SetSymbolLib
from t4gpd.pyqgis.ZoomLib import ZoomLib
QgsProject.instance().clear()
buildings_gdf = GeoDataFrameDemos.districtRoyaleInNantesBuildings()
buildings_layer = AddMemoryLayer(buildings_gdf, 'buildings').run()
SetSymbolLib.setFillSymbol(buildings_layer)
ZoomLib.setExtent(buildings_gdf)
The t4gpd.pyqgis.SetSymbolLib class provides a few static methods to perform different symbologies on the loaded QgsVectorLayer. Finally, the t4gpd.pyqgis.ZoomLib class is used to set the zoom range.